Thio-tag™ Technology
Thio-tag は広島大学大学院 医歯薬学研究科 医薬分子機能化学研究室にて開発されたチオール化合物を捕捉する単核亜鉛錯体分子です。
チオール安定化バッファー

Thio-tag™ Chloride は生理的pH、室温、空気雰囲気下でシステインチオール基などのSH含有化合物を保護し、分析のための選択的安定化剤としてお使いいただけます。
pH3への酸性条件、またはEDTA処理により簡単に解離することができます。
| nTTB-T02 |
|---|
| 1g ¥12,000- |
Cys化合物の安定性
チオール親和性クロマトグラフィー

| 生理pHでチオール化合物の分離精製が可能 | μmol濃度のチオールを捕捉 | チオレートに対する捕捉能はカルボキシレートイオンの 10,000倍 | 簡便な操作で高効率 → 操作時間 ≦ 15分間 |
| nAG1-T01 [チオール捕捉能:1μmol/mL-gel] |
|---|
| 10μL-gel x8 ¥18,000- |
| nAG2-T01 [チオール捕捉能:3.5μmol/mL-gel] |
| 10μL-gel x8 ¥18,000- |
バルク品のご用意もございます。
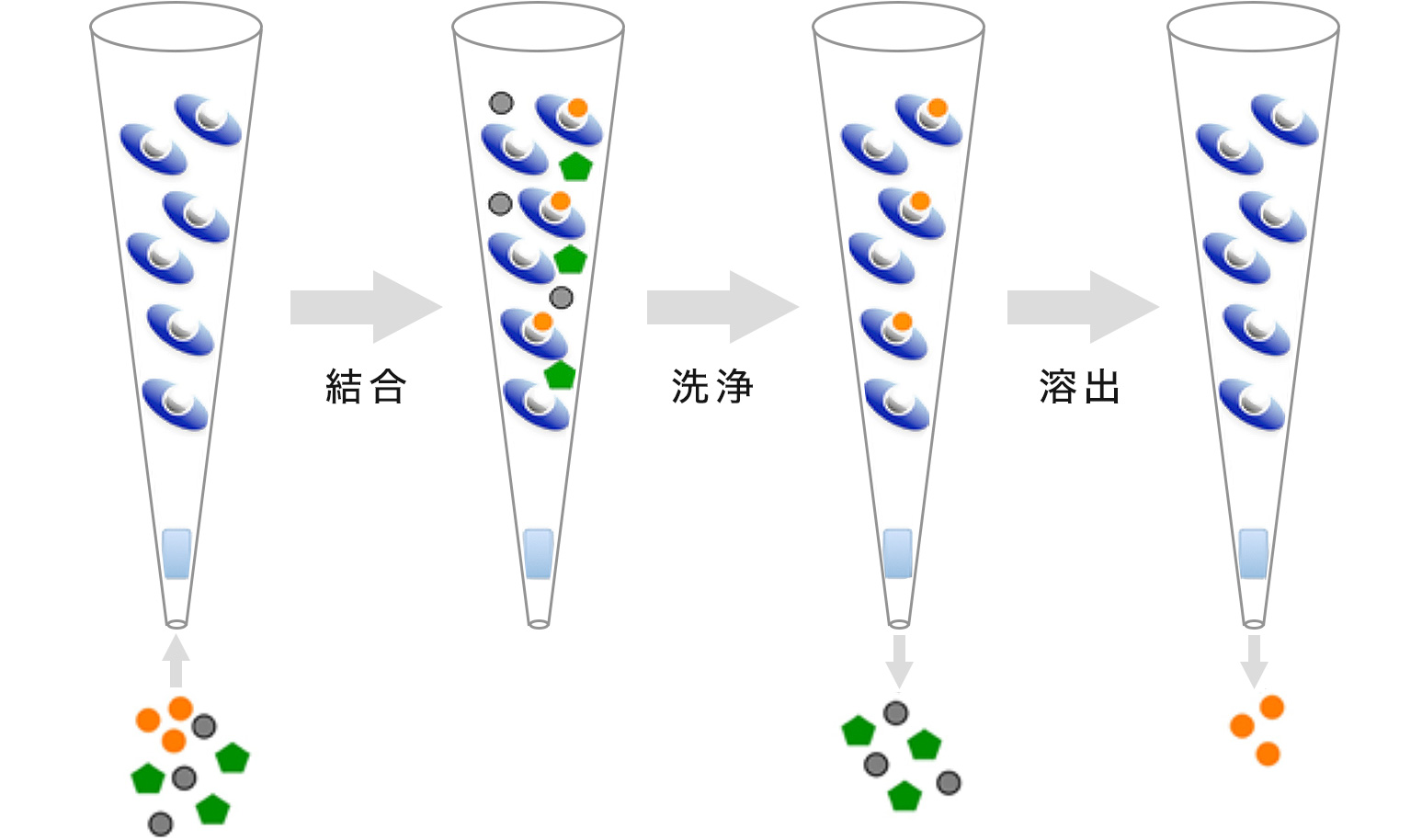
Thio-tag™ Tip 実験例
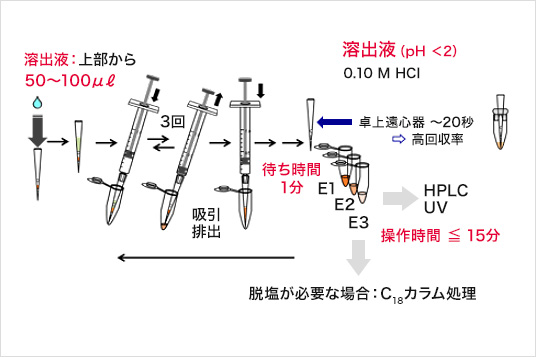
分離操作手順
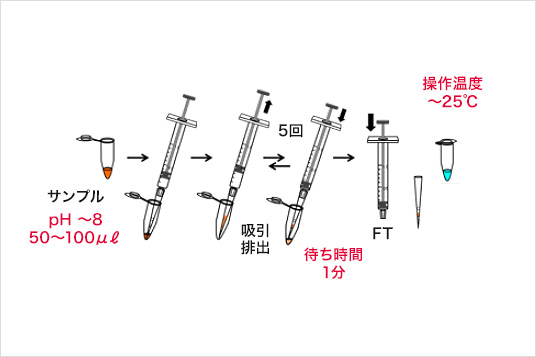
結合
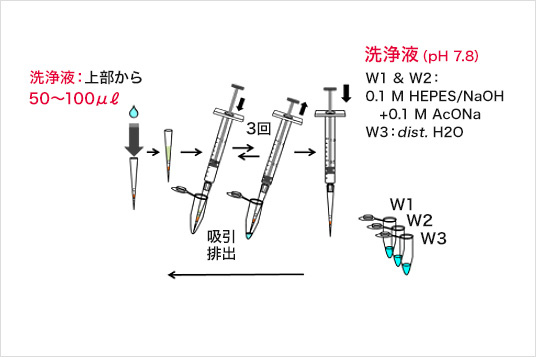
洗浄
溶出
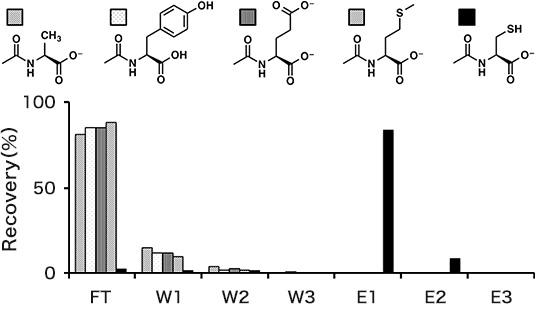
N-アセチルシステインの分離
- ・ Sample solution: 20 nmol each of N-acethyl-amino acids in 50 µL of Sol. B
- ・ Washing solution: Sol. C (50 µL x 2: W1 and W2); distilled water (50 µL: W3)
- ・ Elution solution: Sol. D (50 µL x 3: E1, E2, and E3)
The separation experiment was conducted according to the basic protocol except using Sol. C for preparation of the sample solution. The recoveries of N-acethyl amino acids are shown in Fig. 1. The quantity in the each fraction was analyzed by reversed phase HPLC. The recovery of N-acethylcysteine in the elution fractions was 93%. The other N-acethyl-amino acids were all eliminated in the FT and W1–W3 fractions.
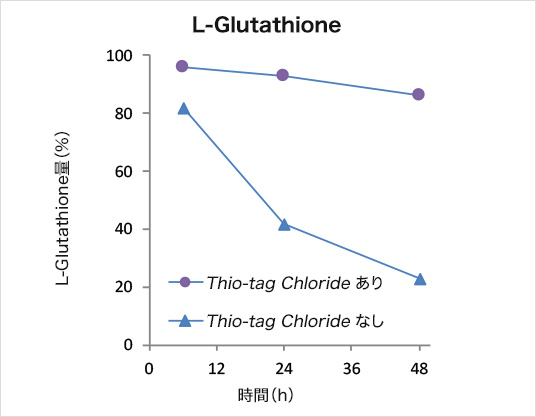
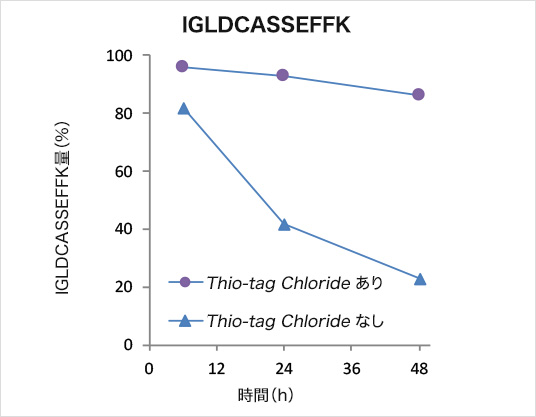
システイン含有ペプチドの選択的分離
- ・ Sample solution: Tryptic digest of 5 nmol β-casein#
- ・ + 6 nmol enolase cysteine peptide (ECP) in 50 µL of pH 7.4 HEPES buffer
- ・ Washing solution: Sol. C (50 µL x 2: W1 and W2); distilled water (50 µL: W3)
- ・ Elution solution: Sol. D (50 µL x 3: E1, E2, and E3)
The separation experiment was conducted in reference to the basic protocol at room temperature and pH 7.4. The total time for the separation experiment was within 15 min. The separation result was analyzed by a reverse phase HPLC with a gradient mode. The cysteine-containing peptide was preferentially eluted in the E1 fraction at recovery of 74%.
#The β-casein digest has no cysteine-containing peptide. A small amount of a monophosphorylated peptide * from β-casein was eluted in the E1 fraction.
ECP: Ile-Gly-Leu-Asp-Cys-Ala-Ser-Ser-Glu-Phe-Phe-Lys
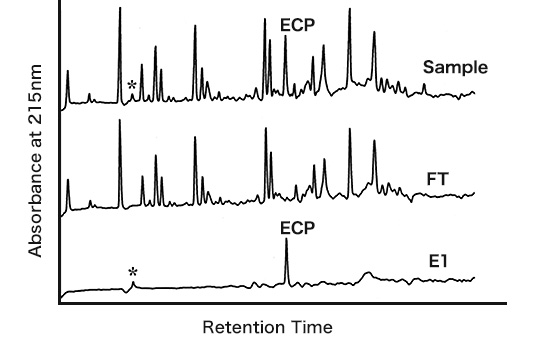
FT is flow-through fraction. E1 is the first elution fraction.
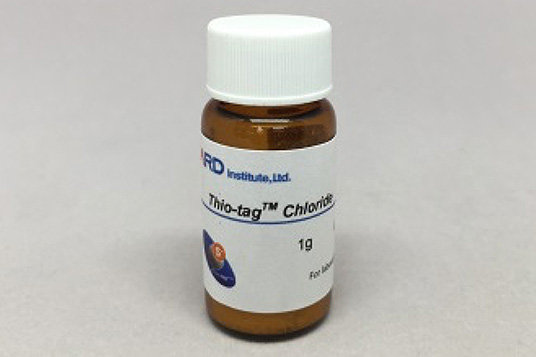
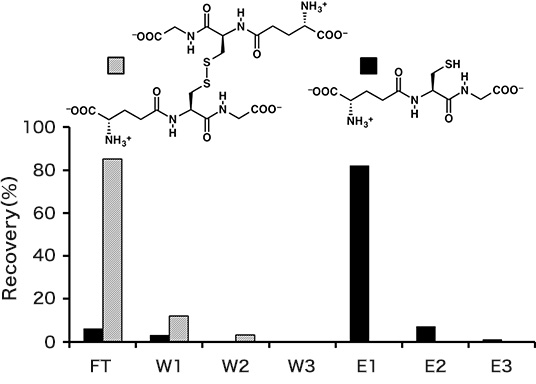
還元型グルタチオンの分離
- ・ Sample solution: 20 nmol of SH-glutathione and 10 nmol of SS-glutathione in 50 µL of Sol. C
- ・ Washing solution: Sol. C (50 µL x 2: W1 and W2); distilled water (50 µL: W3)
- ・ Elution solution: Sol. D (50 µL x 3: E1, E2, and E3)
The separation experiment was conducted according to the basic protocol at room temperature except using Sol. C for preparation of the sample solution. The recoveries of reduced and oxidized species are shown in Fig. 2. The quantity in the each fraction was analyzed by reversed phase HPLC. Total recovery of reduced glutathione was 90% in the elution fractions. The SS-form of glutathione was eliminated in the FT and W1–W3 fractions.
Sol. B (Binding buffer) : 0.10 mol/L HEPES–NaOH (pH 7.8)
Sol. C (Washing buffer) : 0.10 mol/L HEPES–NaOH + 0.10 mol/L CH3COONa (pH 7.8)
Sol. D (Elution buffer) : aqueous 0.10 M HCl
References on Thio-tag™ Chemistry:
imple enrichment of thiol-containing biomolecules by using zinc(II)–cyclen-functionalized magnetic beads, Journal of Separation Scienece, 37, 1601-1609 (2014), H. Fujioka, M. Tsunehiro, M. Kawaguchi, Y. Kuramoto, H. Kurosaki, Y. Hieda, E. Kinoshita-Kikuta, E. Kinoshita, and T. Koike
Role of Zinc(II) in β-Lactamase II: A Model Study with a Zinc(II)-Macrocyclic
Tetraamine (1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane, Cyclen) Complex, Journal of American Chemical Society, 116, 8443-8449 (1994), T. Koike, M. Takamura, and E. Kimura